CBP
Study material Certified Bitcoin Professional (CBP) Exam 2016
Zie ook Princeton
Contents
- 1 Study material Certified Bitcoin Professional (CBP) Exam 2016
- 1.1 Tips & Tricks
- 1.2 History of Money and Ledgerbased Economics
- 1.3 Basic Cryptography
- 1.4 Bitcoin Basics
- 1.5 Mining
- 1.6 Wallets, Clients and Key Management
- 1.7 Bitcoin Commerce
based on CBPStudyGuide
This list is meant to focus your preparation, not provide an exhaustive list of all possible test materials.
For CBP purposes, you don’t need to know how to implement the tech but you will need to understand the basic features, what problems those features solve, and what problems they don’t solve.
Tips & Tricks
What you need to know in Italic
What we offer as links to study material in normal caption
History of Money and Ledgerbased Economics
Centralized Ledgers
Understand what a centralized ledger is and how money has been organized on centralized ledgers in the modern digital economy.
Functions of Currency
Functions of Currency
Distinguish between functions of currencies such as unit of account, store of value, and medium of exchange.
If our 15 million currently available Bitcoins needed to cover 1% of the current world wide money supply then 1 bitcoin would cost $75.000.
Wake up little Suzie.... wake up: Future of blockchain
Wat is macro-economy
- 1. Government
- 2. Consumers
- 3. Producers
- 4. Financial sector
What is money?
- 1. means of transfer
- 2. pricing of value
- 3. stock
- 4. a creditor - debtor relationship
- 5. money is not a thing, a thing can not pop up out of thin air, however a relationship can. (Dirk Bezemer)
How does money arise: Because a new debt relationship had been established (Dirk Bezemer)
FIAT Money
fail, fail and fail again
Distributed Consensus
Define “distributed consensus” and explain what makes bitcoin’s ledger different from centralized ledgers.
What is Bitcoin: 1. It is a money system (capital 'B'), 2. it is a currency (Lowercase 'b'), 3. a family of protocols that makes the system operate
In comprihensable wording
History of Bitcoin
Read the bitcoin protocol white paper. Know about major events affecting bitcoin since its creation such as the failures of early exchanges (who and why) and the birth of altcoins.
PROBLEMS
Of any kind:
- COUNTERPARTY RISK
- THEFT
- FRAUD
- EMBEZZLEMENT
- PHYSICAL LOSS
Exchanges
- Exmo
- Mtgox 750.000BTC 2014
- Mtgox2 750.000BTC 2014
- Mtgox3 750.000BTC 2014
- BitFloor exchange suffered its own break-in in September 2012, losing 24,000 bitcoins when a hacker “accessed an unencrypted backup of wallet keys“. 24.000 BTC 2012
- BTER 2014
- BTER2 & Jua.com 7000BTC 2015
- Bitfinex 120.000BTC aug 2016
- Bitcoinica had already been hacked in March 2012, and lost thousands of bitcoins. But the hack wasn’t enough to bring the company down, and Bitcoincia promised that it would pay back users in full. In May that year, the company was hacked again; that time, it was a killing blow. x000 BTC, 2012
- Bitcurex, a Polish bitcoin exchange, closed its doors temporarily after a hack brought down its Zloty and Euro exchanges. The company lost “between 10 and 20%” of funds. 2014
- Poloniex admitted that 12.3% of its reserves had been stolen due to an unbelievable error in coding (the site failed to check whether users had a negative balance, letting them withdraw more bitcoins than they had). 2014
- Flexcoin a bitcoin bank, lost almost 1000 bitcoins in a hacking attack. 2014
- Canadian Bitcoins, a Canadian bitcoin exchange, revealed it had lost almost $100,000 in the currency when a fraudster opened a chat session with the exchange’s hosting provider. “He claimed to have a problem with a server and asked the attendant to reboot it into recovery mode, allowing him to bypass security on the server,” according to the Ottawa Citizen. At no point in the two-hour session was he asked to prove his identity.
Other hacks and losses
- Allinvain 25.000 BTC 2011
- [Inputs.io] 4.100 BTC 2012
- [BIPS] 1295 BTC 2013
- Picostocks 6000 BTC 2013
- James Howells hard drive on landfill site 7500BTC 2013
- Buy Pizza by Laszlo Hanyecz 10.000BTC 2010
- [Illegal drug bazaar Sheep Marketplace was plundered, either by hackers or insiders, and about $100 million worth of the currency was stolen from customers. 25000BTC 2013
- Silk Road: US DEA officer steals $800.000 2013
Having gained access to the online bazaar, Bridges stole the online currency and tried to pin it on a witness who was cooperating with the investigation, prompting Silk Road founder Ross Ulbricht to take out hits on the witness' life, prosecutors said at Monday's hearing.
Ponzi schemes and frauds
- Bitcoin Savings and Trust was a bitcoin-based Ponzi scheme, that posed as a virtual hedge fund promising to pay high rates of interest to investors. In classic pyramid style, only the first people to invest ever saw those rates of return, as the money of later investors was used to pay off early ones. 150.000BTC 2012
Leocoin
- after research and personal experience:
Onecoin
- after research:
- http://behindmlm.com/companies/onecoin-investment-warning-issued-by-bank-of-hungary/
- http://hotmlmcompanies.com/onecoin-review/
- http://ethanvanderbuilt.com/2015/05/08/onecoin-scam-yes-opinion/ solid research i.m.o.
- https://www.reddit.com/domain/onecoin.eu/ homepage on reddit. Little happens there.
- http://cointelegraph.com/news/one-coin-much-scam-onecoin-exposed-as-global-mlm-ponzi-scheme
Other scam coins
Footnote
- The ICO of Proof of stake public blockchains is sometimes assessed as a Ponzi scheme. That is not true. You could say they are centralized, that could be true. New consensus mechanisms and ways of spreading coins equally in the world are under constant development, e.g. Casper
ALT coins
- Most altcoins are little more than Bitcoin clones, changing only minor characteristics such as its transactions speed, distribution method, or hashing algorithm. Most of these coins do not survive for very long. One exception is Litecoin, which was one of the first altcoins.
Price Derivation
Understand how the price of bitcoin is derived.
Bitcoins are like any other currency: they fluctuate in value relative to other currencies. The value of a bitcoin is constantly changing, and there is no centralised exchange for it. Think of it this way: each time a bitcoin changes ownership from seller to buyer, the two parties need to agree on its price. There is no 'fixed' price. Usually, it's the seller's responsibility to give a fair price to the buyer based on what rate bitcoins are being traded in elsewhere. The difference between bitcoins and other currencies is that there is no centralised bank that prints the currency and sets relative values. Through transactions, the value of bitcoin fluctuates through supply and demand.
Basic Cryptography
Terms and Definitions
Define and accurately use basic cryptographic terms such as cryptography, encryption algorithm, decryption algorithm, symmetric vs. asymmetric encryption, cipher vs. plain text.
Basic Terminology
- Encryption is the process of turning a clear-text message (Plaintext) into a data stream which looks like a meaningless and random sequence of bits (ciphertext). The process of turning ciphertext back into plaintext is called decryption.
- Cryptography deals with making communications secure. Cryptoanalysis deals with breaking ciphertext, that is, recovering plaintext without knowing the key. Cryptology is a branch of mathematics which deals with both cryptography and cryptoanalysis.
- A cryptographic algorithm, also known as a cipher, is a mathematical function which uses plaintext as the input and produces ciphertext as the output and vice versa.
- All modern ciphers use keys together with plaintext as the input to produce ciphertext. The same or a different key is supplied to the decryption function to recover plaintext from ciphertext. The details of a cryptographic algorithm are usually made public. It is the key that the security of a modern cipher lies in, not the details of the cipher.
- Symmetric algorithms use the same key for encryption and decryption. These algorithms require that both the sender and receiver agree on a key before they can exchange messages securely.
- Some symmetric algorithms operate on 1 bit (or sometimes 1 byte) of plaintext at a time. They are called stream ciphers. Other algorithms operate on blocks of bits at a time. They are called block ciphers. Most modern block ciphers use the block size of 64 bits.
- Public-key algorithms (also known as asymmetric algorithms) use two different keys (a key pair) for encryption and decryption. The keys in a key pair are mathematically related, but it is computationally infeasible to deduce one key from the other. These algorithms are called "public-key" because the encryption key can be made public. Anyone can use the public key to encrypt a message, but only the owner of the corresponding private key can decrypt it.
- Some public-key algorithms such as RSA allow the process to work in the opposite direction as well: a message can be encrypted with a private key and decrypted with the corresponding public key. If Alice (or anyone else) can decrypt a message with Bob's public key she knows that the message must have come from Bob because no one else has Bob's private key. Digital signatures work this way.
Hash Functions
Explain the purpose of hash functions, how they are used in bitcoin, and how their inputs are related to their outputs.
Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
Distinguish between symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms. Understand the principles of asymmetric encryption and the impact it has on key exchange.
Digital Signatures
Understand the basics of digital signatures, why and how they are used in bitcoin. Understand the relationship between digital signatures and asymmetric keys.
- DuckDuckGo - Digital Signatures
- Public Key Encryption and Digital Signature: How do they work? by CGI
Bitcoin Basics
Bitcoin Community
Understand how users, advocates, developers, businesses, and governments impact the Bitcoin Protocol. Explain what types of institutions are actively involved in promoting, maintaining, or lobbying on behalf of the industry.
Governance
Government
Business
Developers
Bitcoin Addresses and Keys
Understand how bitcoin addresses and keys are generated. Explain the relationship between bitcoin addresses, public keys, and private keys; distinguish between them and describe the primary use of each. In terms of addresses and keys, describe how funds are accessed and transferred on the bitcoin network.
Bitcoin Addresses and Keys
- bitcoin.it - Address
- Bitcoin Magazine - What is an Address and how do you sign it?
- Keys, Addresses and Wallets
- Derive Public Key from Private Key
Video instruction
Bitcoin Transactions
Describe a bitcoin transaction in terms of inputs and outputs. Explain why a simple bitcoin transaction is irreversible. Understand the basics of transaction fees.
Bitcoin Blockchain Ledger
Explain how bitcoin’s blockchain functions as a public ledger. What information is public?
bitcoin the Unit
Know and understand the denominations of bitcoin and their relation to one another (e.g. millibit, satoshi). Explain the difference between Bitcoin (capitalized B) and bitcoin. Recognize other commonly used symbols referring to bitcoin as a digital currency.
Bitcoin the Network
Understand network basics such as how the network is connected and the importance of independent nodes in the structure. Explain common network attacks (such as DDoS) and how the network is secured from these types of attacks.
Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs)
What is a BIP? Explain the basic process of submitting, evaluating, and implementing a BIP. Review Github Bitcoin Improvement Proposals.
Three kinds
- Standards Track BIPs - Changes to the network protocol, block or transaction validation, or anything affecting interoperability.
- Informational BIPs - Design issues, general guidelines. This type of BIP is NOT for proposing new features and do not represent community consensus
- Process BIPs - Describes or proposes a change in process. Similar to Standards BIPs but apply outside the Bitcoin protocol.
Links
How it works
People wishing to submit BIPs, first should propose their idea or document to the mailing list. After discussion they should email Luke Dashjr <luke_bipeditor@dashjr.org>. After copy-editing and acceptance, it will be published here.
We are fairly liberal with approving BIPs, and try not to be too involved in decision making on behalf of the community. The exception is in very rare cases of dispute resolution when a decision is contentious and cannot be agreed upon. In those cases, the conservative option will always be preferred.
Having a BIP here does not make it a formally accepted standard until its status becomes Active. For a BIP to become Active requires the mutual consent of the community.
Those proposing changes should consider that ultimately consent may rest with the consensus of the Bitcoin users (see also: economic majority).
Economic_majority : So the ability for a protocol change to be successfully implemented ultimately rests with those who accept bitcoins in exchange for value. Generally those will be the merchants. If the economic majority doesn't run full nodes Bitcoin is dead
Abstract: propose their idea -> email Luke Dashjr -> edit&acceptance -> dispute resolution conservative -> Active if mutual consent
Buying and Selling bitcoin
What are the different ways users can buy and sell bitcoin? What is a bitcoin exchange? Who uses bitcoin exchanges and why? Understand the risks of storing bitcoin on exchanges and identify best practices for storing bitcoin.
Middleman resellers
Exchanges
Craigslist for bitcoins
Blockchain Explorers
What is a blockchain explorer? How can they be used to trace payments?
Block_chain_browsers
Bitcoin blockchain
Ethereum blockchain
Ethereum CLASSIC
Old
UTXOs
What is an Unspent Transaction Output? How do these affect transactions you send and the change that is leftover from your transaction?
- Mark Erhardt Milan 2016 about his research on UTXO's in Bitcoin
- UTXO made simple on Reddit
Change addresses
- ways to lose money with bitcoin change addresses
- Restoring the backup only restored empty addresses
Miscommunication example
Why is this explanation wrong and why? -> UTXO explanation
Mining
Purpose and Function
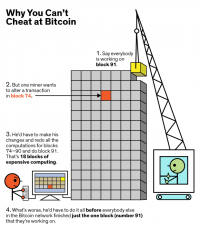
Explain the basic value that miners provide to the bitcoin network. How are new bitcoins created?
Algorithm
For Bitcoin mining algorithm, define and describe the following: difficulty adjustment, hashing algorithm, coinbase transaction, coinbase transaction size, nonce, and block reward.
- Escape Velocity - Bitcoin Mining Explained Like You're Five: Part 1
- Escape Velocity - Bitcoin Mining Explained Like You're Five: Part 2
Mining Pools
What is a mining pool? What is a centralized mining pool? What is a P2P pool? Compare and contrast. From the perspective of the network: what are the advantages and disadvantages of pools compared to single miners? From the perspective of a miner: what criteria should I consider when choosing a mining pool?
Mining Hardware
What is the most popular hardware used today for bitcoin mining? Describe the differences between CPU, GPU, and ASIC hardware.
Security and Centralization
Under what conditions is a 51% attack feasible? Explain what a potential attacker can and cannot do with a large proportion of network hashing power. Understand the relationship between mining pools, specialized hardware, and the likelihood of attacks.
Wallets, Clients and Key Management
Wallet Types
What is a bitcoin wallet and how are they used? Explain the differences between software, web, hot/cold, paper, brain, hardware, multisig, HD, and HDM wallets.
- Bitcoin Book - The Bitcoin Wallet
- 14 best Bitcoin wallets and the reasons why
HD Wallets
The Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) key creation and transfer protocol (BIP32), which allows creating child keys from parent keys in a hierarchy. Wallets using the HD protocol are called HD wallets.
HDM wallets
Multisig added to HD
Use the concept of an Oracle, originally coined by Alan Turing and adapted to Bitcoin by Mike Hearn. An Oracle in this context is a trusted third party that signs transactions only when certain conditions are met, in order to enforce security or implement other functions.
HDM wallets with a third-party Oracle can provide security while not compromising usability. The user retains custody of 2 out of 3 keys, and does not experience counterparty risk, while still relying on a trustworthy third party to countersign normal transactions. The trusted third party, an Oracle, vets transactions to protect a user from theft, fraud and risk without being able to take possession or control of funds. The Oracle can also alert the user to wallet compromise and merchants with negative reputation. For more about 2-of-3 multisignature wallets, please see BIP-0011 and the Storage white paper.
- Copay is an example of a HD multisig wallet. More info: https://copay.io/
- www.blocktrail.com offers a simple API for a HDM Wallet
Bitcoin Clients
Describe the difference between lightweight and full clients. What is Simplified Payment Validation (SPV) and how is it used in lightweight clients?
Deterministic Wallets (BIP32)
What are deterministic wallets? What advantages do they have over “Just a Bunch of Keys” wallets?
The Bitcoin reference client uses randomly generated keys. In order to avoid the necessity for a backup after every transaction, (by default) 100 keys are cached in a pool of reserve keys. Still, these wallets are not intended to be shared and used on several systems simultaneously. They support hiding their private keys by using the wallet encrypt feature and not sharing the password, but such "neutered" wallets lose the power to generate public keys as well.
Deterministic wallets do not require such frequent backups, and elliptic curve mathematics permit schemes where one can calculate the public keys without revealing the private keys. This permits for example a webshop business to let its webserver generate fresh addresses (public key hashes) for each order or for each customer, without giving the webserver access to the corresponding private keys (which are required for spending the received funds).
However, deterministic wallets typically consist of a single "chain" of keypairs. The fact that there is only one chain means that sharing a wallet happens on an all-or-nothing basis. However, in some cases one only wants some (public) keys to be shared and recoverable. In the example of a webshop, the webserver does not need access to all public keys of the merchant's wallet; only to those addresses which are used to receive customer's payments, and not for example the change addresses that are generated when the merchant spends money. Hierarchical deterministic wallets allow such selective sharing by supporting multiple keypair chains, derived from a single root.
PassphraseEncrypted Wallets (BIP38)
What are passphrase encrypted wallets? What advantages do they have over plain wallets?
Motivation BIP 0038
The motivation to make this proposal stems from observations of the way physical bitcoins and paper wallets are used.
An issuer of physical bitcoins must be trustworthy and trusted. Even if trustworthy, users are rightful to be skeptical about a third party with theoretical access to take their funds. A physical bitcoin that cannot be compromised by its issuer is always more intrinsically valuable than one that can.
A two-factor physical bitcoin solution is highly useful to individuals and organizations wishing to securely own bitcoins without any risk of electronic theft and without the responsibility of climbing the technological learning curve necessary to produce such an environment themselves. Two-factor physical bitcoins allow a secure storage solution to be put in a box and sold on the open market, greatly enlarging the number of people who are able to securely store bitcoins.
User stories that ask for BIP 0038
- User story: As a Bitcoin user who uses paper wallets, I would like the ability to add encryption, so that my Bitcoin paper storage can be two factor: something I have plus something I know.
- User story: As a Bitcoin user who would like to pay a person or a company with a private key, I do not want to worry that any part of the communication path may result in the interception of the key and theft of my funds. I would prefer to offer an encrypted private key, and then follow it up with the password using a different communication channel (e.g. a phone call or SMS).
- User story: (EC-multiplied keys) As a user of physical bitcoins, I would like a third party to be able to create password-protected Bitcoin private keys for me, without them knowing the password, so I can benefit from the physical bitcoin without the issuer having access to the private key. I would like to be able to choose a password whose minimum length and required format does not preclude me from memorizing it or engraving it on my physical bitcoin, without exposing me to an undue risk of password cracking and/or theft by the manufacturer of the item.
- User story: (EC multiplied keys) As a user of paper wallets, I would like the ability to generate a large number of Bitcoin addresses protected by the same password, while enjoying a high degree of security (highly expensive scrypt parameters), but without having to incur the scrypt delay for each address I generate.
Backups, Importing and Exporting
What is Wallet Import Format (WIF)? Describe the process of backing up private keys and restoring them to the same or new wallets.
- WIF is a way of encoding a private ECDSA key so as to make it easier to copy.
- Bitcoin.it - Securing Your Wallet
- Securing Your Wallet
Bitcoin Commerce
Bitcoin Merchants
Describe how merchants can begin accepting bitcoin for products and services.
Bitcoin Payment Processors
What is a payment processor? What services do they provide?
What is the added value of a payment processor=
One of the most popular services provided by these payment processors is the instant conversion of Bitcoin (BTC) to your local fiat currency (like USD for example). This is important for many businesses because most businesses which accept Bitcoin payments still have to pay all of their own costs and buy stock using fiat money, so changes in the exchange rate between Bitcoin and the businesses local currency could lead to losses if the BTC accepted as payment is not instantly converted into fiat.
Payment processors also provide you with all of the tools and reports that you need to make accepting Bitcoin payments as simple and convenient as possible without you having to develop your own software solution.
Secure Payment Protocol (BIP70)
What is the Secure Payment Protocol and how is it used on the network? How can you identify secure payments compared with standard payments?
What is Secure Payment Protocol
This BIP describes a protocol for communication between a merchant and their customer, enabling both a better customer experience and better security against man-in-the-middle attacks on the payment process.
better customer experience
- Human-readable, secure payment destinations-- customers will be asked to authorize payment to "example.com" instead of an inscrutable, 34-character bitcoin address.
- Secure proof of payment, which the customer can use in case of a dispute with the merchant.
better security against man-in-the-middle
- Resistance from man-in-the-middle attacks that replace a merchant's bitcoin address with an attacker's address before a transaction is authorized with a hardware wallet.
Both
- 3-way-handshake: Payment received messages, so the customer knows immediately that the merchant has received, and has processed (or is processing) their payment.
- Refund addresses, automatically given to the merchant by the customer's wallet software, so merchants do not have to contact customers before refunding overpayments or orders that cannot be fulfilled for some reason.